Unleashing the Power of AI for Dynamic Learning in the Classroom

Education as 'Transfer' vs 'Dynamic Learning'
Are you looking to unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in your classroom? We have an innovative approach that goes beyond just knowledge transfer, paving the way for dynamic learning experiences. Don't miss our related practical advice for applying these approaches to AI in the classroom (coming soon).
In a thought-provoking paper on integrating AI into education, Mollick and Mollick kick off their analysis with this:
"The goal of education is to effect a permanent change in knowledge. One of the hardest problems educators encounter is the problem of transfer. Transfer is the ability to apply the knowledge, skills, and strategies learned in the classroom, outside of the classroom. Transfer is difficult because it requires deep understanding of a concept. Initially, when students learn about a new concept in one context, they often fail to recognize that concept when they encounter it again in a new context."
While the authors provide good suggestions for how AI can improve education, and specifically the problem of "transfer" (knowledge acquisition and retention), we believe there's more to the story. Sure, there are instances when the teacher knows something, like how to perform long division, and the students don't, making it valuable for them to learn the skill.
However, we contend that the real power of AI in education lies in fostering dynamic learning experiences. Consider long division as an example. Students might struggle to grasp this concept if it's presented as a set of arbitrary, abstract rules. Dynamic learning, on the other hand, embeds knowledge acquisition within students' real-life experiences. In this context, long division becomes a practical tool to help students achieve personal goals, such as adjusting recipe measurements or calculating weekly savings for a desired toy. To truly harness AI's potential in education, we must embrace a a broader conception of education:
What is the goal of education?
Instead of diving into a philosophical debate on the nature of education, let's explore a more comprehensive definition provided by GPT, which goes beyond mere knowledge transfer:
Acquisition of Knowledge and Skills: Education serves the purpose of providing individuals with the knowledge, skills, and competencies needed to succeed in their chosen field or career.
Personal Development: Education also serves the purpose of personal development, helping individuals to develop their intellectual, social, emotional, and physical abilities to their fullest potential.
Socialization and Civic Responsibility: Education serves the purpose of socialization and civic responsibility, preparing individuals to become responsible and engaged members of society.
Cultural Preservation: Education serves the purpose of preserving culture, history, and traditions by transmitting them from one generation to the next.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: Education serves the purpose of developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, enabling individuals to think creatively, analyze situations, and make informed decisions.
This perspective shifts the conversation from simply memorizing facts or mastering skills to cultivating well-rounded individuals. A high-quality education fosters intellectual curiosity, social awareness, emotional intelligence, and physical well-being, without losing sight of the utility of acquiring knowledge and skills for career success.
Embracing Dynamic Learning: Active, Experiential, and Contextual Education
We use the term "dynamic learning" to describe a collection of educational approaches that focus on active, experiential, and contextually relevant learning experiences. These experiences aim to support learners in achieving their goals and solving real-world problems. Dynamic learning is inspired by theories such as:
Constructivism
Dynamic learning aligns with constructivist theories, highlighting the importance of learners actively engaging with their environment to construct their own knowledge. Learners are encouraged to experiment, explore, and discover knowledge through hands-on activities and problem-solving.
Experiential Learning
Dynamic learning resonates with experiential learning theories, emphasizing learning through direct experience and reflection. Learners are given real-world problems to solve and encouraged to reflect on their experiences, deepening their understanding and building new knowledge.
Situated Learning
Dynamic learning is in tune with situated learning theories, stressing the importance of learning in context. Learners engage in experiences relevant to their lives and interests, allowing them to connect new knowledge to their existing knowledge and experiences.
Personalized Learning
Dynamic learning aligns with personalized learning theories, highlighting the need to tailor learning experiences to individual learners' needs and interests. Learners have the opportunity to set their own learning goals, explore their interests, and receive personalized feedback and support.
Dynamic Learning and Pedagogy
By embracing dynamic learning, educators can create more engaging, coherent, and meaningful learning experiences that cater to the diverse needs and interests of their students. As a result, they will empower well-rounded individuals capable of thriving in today's rapidly changing world.
For fun, let's ask GPT itself how it understands some of the main pedagogical theories! Here is GPT-4s placement of different pedagogical schools on the axes of "Teacher- vs Student-Centered Approachs" and "Content- vs Skill-Centered Approaches".
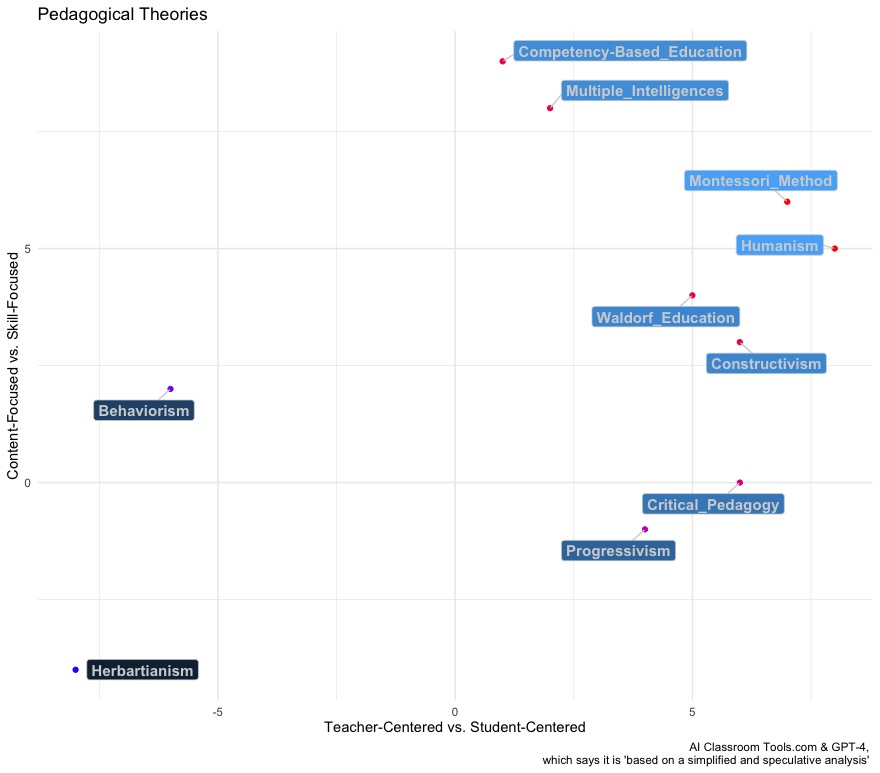
Coming up next - practical skills for applying the Dynamic Learning approach!
References:
Mollick, Ethan R. and Mollick, Lilach, New Modes of Learning Enabled by AI Chatbots: Three Methods and Assignments (December 13, 2022). Available at SSRN